What is an Exosome?
Exosomes are small vesicles, 30-150 nanometers in diameter, with a lipid membrane that cells release, carrying genetic information, growth factors, and proteins. Exosomes are vesicles secreted by stem cells, but they are not cells themselves. Their primary function is to facilitate communication between cells. These vesicles carry biomolecules such as proteins, lipids, and RNA.
Exosomes are not found in food. Therefore, they cannot be ingested through diet. Exosomes are produced by the body’s cells. However, a healthy and balanced diet allows cells to maintain healthy function and increases their exosome production.
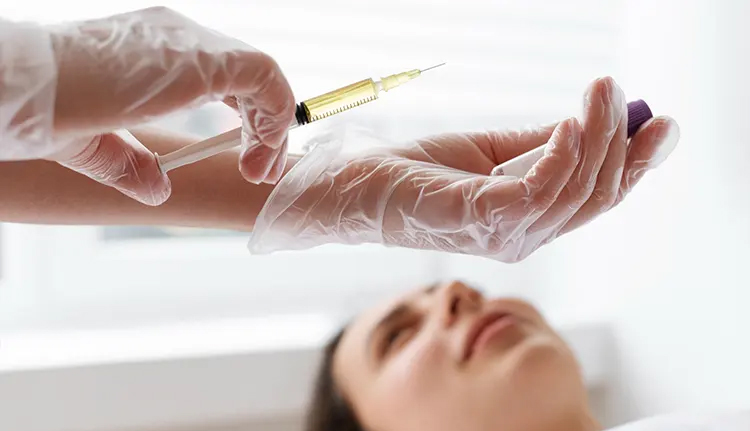
How to Obtain Exosomes?
Exosomes used for therapeutic purposes are produced in laboratories approved by the Ministry of Health and comply with GMP standards, and undergo 10 different quality and characterization tests. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal small cells are propagated using appropriate culture methods, and once they reach sufficient numbers, they are allowed to produce exosomes. The resulting exosomes are purified and stored as a homogeneous suspension in a sterile, cold-chain manner.
Where Are Exosomes Used?
Dermatology: Skin rejuvenation, anti-aging treatments, scars, skin blemishes, hair loss, collagen production, burn treatment, atopic dermatitis, and eczema.
Cardiology: Regeneration of heart tissue after a heart attack, angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation).
Orthopedics: Joint pain, cartilage damage, osteoporosis, and inflammation.
Oncology: Focusing chemotherapy drugs directly on tumors as carriers.
Neurology: Exosomes are used in the regeneration of nerve cells and the repair of damaged tissue in diseases such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and stroke.
What are the Sources of Exosome Stem Cells?
Volunteer human donors may be of animal or plant origin.
What is Exosome Used For? What is It Good For?
Exosomes, which have a wide range of uses in aesthetic and medical fields, are used to treat skin and scalp conditions.
Skin Rejuvenation and Anti-Aging Treatment: By increasing collagen production, they reduce wrinkles and fine lines and increase skin tone. They reduce the appearance of skin blemishes.
Wound and Scar Treatment: Exosomes have a high potential for cell regeneration and repair. They exhibit anti-inflammatory effects. They reduce apoptosis in tissues damaged by disease or injury. By increasing collagen cross-linking, they promote healing in scars closer to normal tissue.
Hair Loss Treatment: They increase the number of hair follicles in the growth phase. Thanks to their growth factors and protein content, exosomes revitalize hair follicles. They prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.

Who Cannot Get Exosome Therapy?
While it’s a method that promotes cell regeneration, it may not be suitable for everyone. A physician should evaluate the individual’s general health before treatment. Exosome therapy is not suitable for pregnant women, nursing mothers, those with active infections, bleeding disorders, or autoimmune diseases.
What are the Side Effects of Exosomes?
Risk of infection in non-sterile conditions
Mild edema and redness in the injection area Temporary
tenderness and pain
Rare allergic reactions
How to Administer Exosomes?
In exosome therapy, exosomes derived from stem cells are injected dermally into the treatment area using microneedling, or mesotherapy. Topical applications are also available in the aesthetic field. Systematic treatments are also available in other areas of medicine.
When Does Exosome Take Effect?
The time required for the effects of treatment to be seen varies between 3 and 4 months. Skin repair continues for 6-8 months.
How Many Exosome Sessions Should Be Done?
Depending on the treatment area and indication, 1 to 3 sessions are recommended.